

1 Overview:
Wire mesh demister (also known as wire mesh demister, foam trap) is an efficient gas-liquid separation device, widely used in chemical, petroleum, sulfuric acid, medicine, light industry, metallurgy, machinery, environmental protection and other industries In the production equipment of ethylene, synthetic ammonia, chemical fiber, etc. imported from abroad in my country, wire mesh defoaming is also used as a gas-liquid separation device.
When the gas with mist passes through the screen at a certain gas velocity, the mist collides with the screen and is attached to the surface of the screen. The diffusion of the mist on the surface of the filament and the gravitational settlement of the mist make the mist agglomerate into larger droplets and be removed. After the gas passes through the wire mesh demister, there is basically no mist.
Separate the mist in the gas to improve operating conditions, optimize process indicators, reduce equipment corrosion, extend equipment service life, increase processing capacity and recover valuable materials, protect the environment, and reduce air pollution.
Simple structure, small size, high defoaming efficiency, low resistance, light weight, convenient installation, operation, and maintenance. The wire mesh defoamer has a collection efficiency of 98%-100% for mist with a particle size of ≥5um, while the gas passes through The pressure drop of the demister is very small, only 250-500Pa, which is beneficial to improve the production intensity of the packed tower.
2. Working principle:
The diameter of the dispersed liquid droplets in the gas encountered in the usual chemical operation is about 0.1-5000um. Generally, the particles with a diameter of 100um or more settle down quickly, and the separation problem is easy to solve. Usually, the liquid with a diameter greater than 50um Droplets can be separated by gravity sedimentation; droplets above 5um can be separated by inertial collision and centrifugal separation; for smaller mist, try to make it aggregate to form larger particles, or use fiber filters and electrostatic demisters.
The wire mesh demister is mainly used to separate droplets with a diameter greater than 3um-5um. The working principle is shown in the figure. When the gas with liquid foam rises at a certain speed and passes through the wire mesh on the grid, due to the inertial effect of the rising liquid foam, the liquid foam collides with the filament and adheres to the surface of the filament. The liquid foam on the surface of the filament further diffuses and the gravity sedimentation of the liquid foam itself makes the liquid foam form larger droplets and flow along the filament to its interweaving. Due to the wettability of the filaments, the surface tension of the liquid and the capillary action of the filaments, the droplets become larger and larger until their own gravity exceeds the combined force of the rising buoyancy of the gas and the surface tension of the liquid, they are separated and fall. Flow to the downstream equipment of the container. As long as the operating gas speed and other conditions are selected properly, after the gas passes through the wire mesh demister, its defoaming efficiency can reach more than 97%, which can completely achieve the purpose of removing fog.
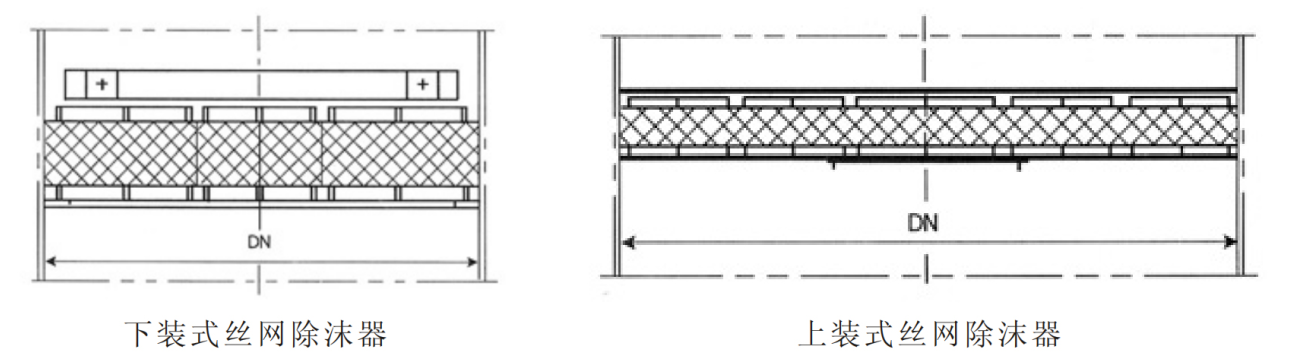
National standard: HG/T21618-1998 is based on the original Ministry of Industry standard (HG5-1404-81, HG5-1405-81, HG5-1406-81), combined with the actual use experience of the wire mesh demister and the introduction of the device The advanced technology is revised, and the three standards are merged into one standard, which is divided into only the top loading type and the bottom loading type.
3. Net block thickness and net block structure:
The thickness of the three types of net blocks are 100mm and 150mm.
The net block structure has two types: disc shape and strip shape.
(Note: a. In general, each tower is installed with two layers of net blocks, the reference interval: 500-1200mm in the upper space; 500-1000mm in the lower space, 500-1200mm between the two layers; b. Suggestion: a strip net block structure with a diameter of 600mm .)
Material selection:
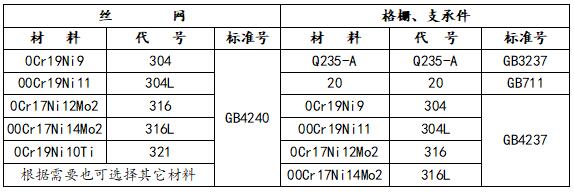
The non-steel mesh materials that can be selected for the wire mesh demister: domestic materials mainly include NS-80, 0Crl8Ni12Mo2Ti, 00Cr17Ni14Mo2, SS920; imported materials include 316L, 317L, 904L, No. 20 alloy, SX alloy, etc. Among them, imported 316L and NS-80 made in China are the commonly used wire mesh materials for demisters in sulfuric acid. For the grid material, ordinary carbon steel is generally not suitable for sulfuric acid, and IC18Ni9Ti or higher stainless steel can be used.
Purpose: The demister (demister) is used to separate the liquid droplets entrained by the gas in the tower to ensure the mass transfer efficiency, reduce the loss of valuable materials and improve the operation of the compressor after the tower. Generally, a wire is installed on the top of the tower. Net demister. It can effectively remove 3--5um droplets. If a demister is installed between the trays, it can not only ensure the mass transfer efficiency of the trays, but also reduce the plate spacing. Therefore, the wire mesh demister is mainly used for gas-liquid separation. It can also be an air filter for gas separation. In addition, the wire mesh can also be used as a buffer for various meters in the meter industry, electronic shields to prevent radio wave interference, etc.
Table 1. Gas-liquid filter type and basic parameters used in wire mesh demister
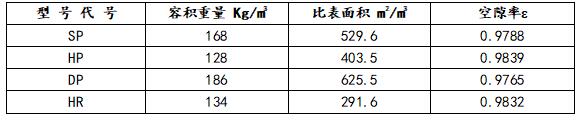
Table 2. Commonly used materials for wire mesh demisters
Features of wire mesh defogger:
1.Simple structure and light weight.
2. Large void ratio and small pressure drop
3. Large contact surface area and high defoaming efficiency
4. Convenient installation, operation and maintenance
5. Long service life
Purpose: Used for filtering, screening, catalyst and distillation, evaporation, absorption and other processes entrained in the gas dust particles, mist droplets
- Previous Article: Wave-in-wave stainless steel structured packing
- Next Article: Stainless steel orifice double-wave corrugated packing