>>Working principle:
In the chemical process, the gas from various gas-liquid contact equipment often entrains many liquid droplets when leaving the equipment, such as tower equipment, evaporators, etc. It is generally required to separate the liquid droplets entrained by the gas so as not to affect the quality of the gas or the operation of the next process.
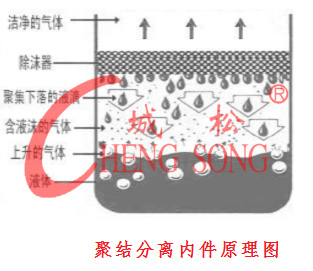
The mechanisms for separating droplets or mist from gas include gravity sedimentation, inertial collision, centrifugal separation, diffusion deposition of Brownian motion, and electrostatic attraction. The coalescing and separating internals are a typical product in inertial collision defoaming, and it is an efficient gas-liquid separation equipment. It has the characteristics of high defoaming efficiency, simple structure, large porosity, small pressure drop, light weight, and convenient installation, operation and maintenance.
When the gas separates the internal parts through coalescence from bottom to top, due to the inertial effect and the surface of the wire mesh, the mist immediately gathers and expands on the surface of the filament. The gravitational force generated by the weight of the continuously growing droplet exceeds the speed and speed of the gas. When the combined force of the liquid surface stretches, the droplet falls. It is often used in towers, evaporators and separators in industry.

1. Purify the gas itself
2. Remove harmful liquids to ensure the normal operation of subsequent processes
3. Prevent damage to subsequent equipment
4. Avoid unqualified air emissions
5. The valuable liquid produced during the recovery process.
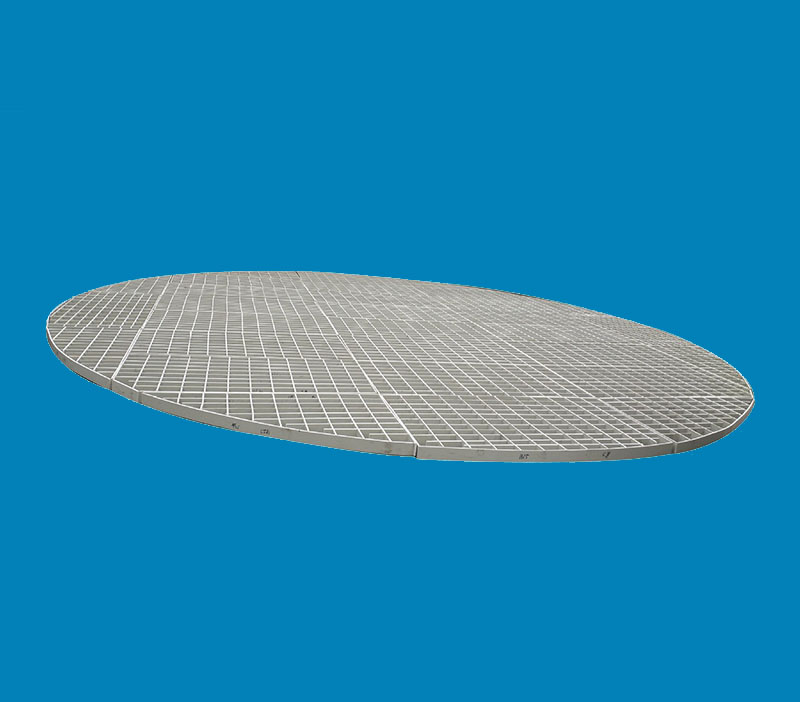
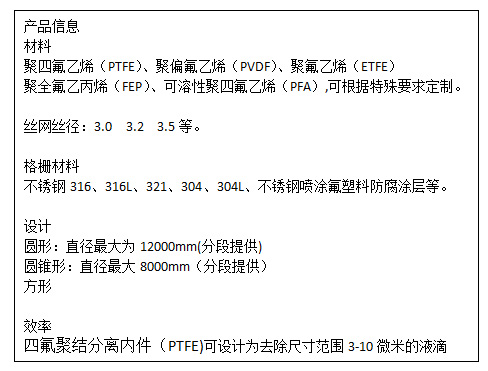
Provide you with various types of PTFE coalescing and separating internals (PTFE), the specifications are determined by the free volume, the surface area of the package, the thickness of the thread and the height of the package.
The PTFE coalescing and separating internals (PTFE) can also be used downstream of the vane separator to remove finer droplets under low-speed conditions (processing conditions with high turndown ratios).
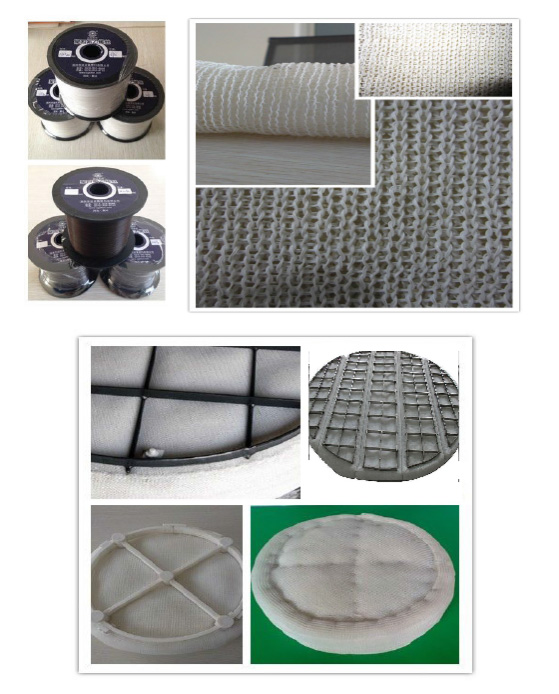


Classification:
PTFE coalescing and separating internals for vertical air flow (as separator)
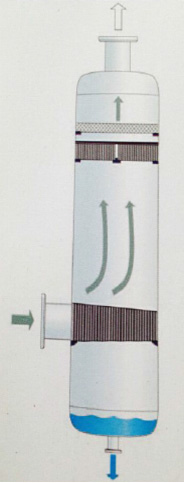
The droplets entrained in the airflow impact on the tow of the screen. The smaller droplets flow around the tow and are carried away by the airflow, while the larger droplets merge together and drop under the action of gravity. Can be collected and removed.
Demisting of air flow with low to medium liquid load (lower air velocity)
PTFE coalescing and separating internal parts can remove droplets in the range of 3-10 microns.
PTFE coalescing and separating internals for horizontal airflow (as coalescer)
The wire mesh type coalescer can also be used as a horizontal air flow coalescer, which can form larger droplets from small droplets. Larger diameter droplets then gather in the airflow and impact the subsequent blade separator, and the liquid is separated and recovered. These droplets are finally completely removed in the blade separator.
Constant water removal efficiency in high-speed adjustment ratio applications
Ensure very low liquid residual content, achieve ideal follow-up parts and the highest product recovery rate
Very useful for liquid recovery systems with droplet sizes in the range of 3-5 microns
Suitable for high liquid loads-efficient applications
The combination of the wire mesh type agglomerator and the blade type separator can remove droplets in the range of 2-3 microns.
typical application:
Sulfuric acid plant, PTA, LNG plant/synthetic ammonia plant, chlorine production industry, acetic acid, hydrofluoric acid, fluoride salt and liquid sulfur removal, fan, compressor protection, etc.
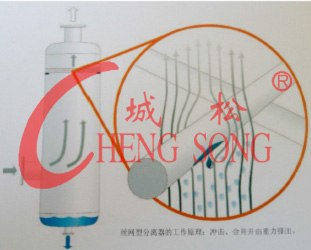
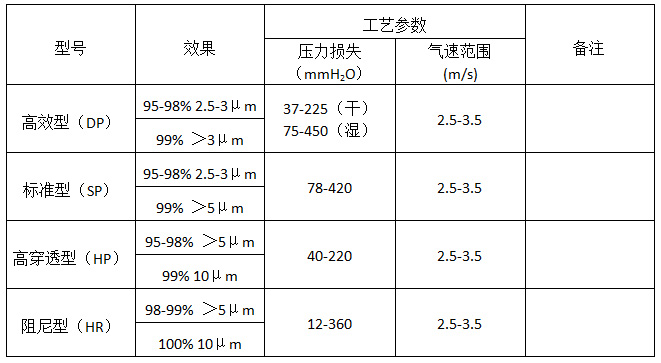
According to the type of wire mesh weaving, it is divided into four main types: SP, HP, DP, and HR. The defoaming efficiency and pressure loss are shown in the following table:
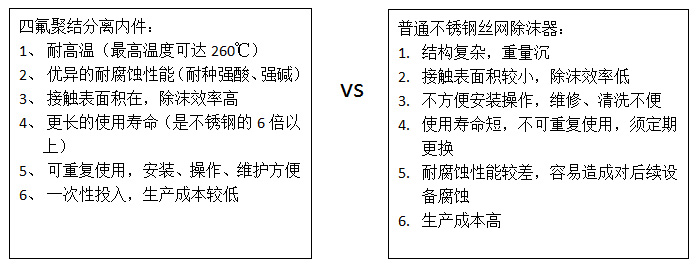
Application characteristics of PTFE coalescing and separating internal parts in industry and comparison with stainless steel wire mesh demister:
- Previous Article: PTFE packing
- Next Article: No Record