one. Product Features
Arsenic removal filter is mainly used to remove arsenic in the system and purify water quality; it can also be used to decolor and deodorize water.
two. Scope of application
It is often used as a dedicated equipment for centralized removal of arsenic ions in drinking water that uses groundwater as a source of water.
three. Features
1. The unique multi-filter chamber structure can realize online backwashing (filtering, draining and backwashing at the same time).
2. At the same time, the separate regeneration treatment process is operated, which greatly improves the utilization rate of equipment and filter material.
3. According to the water pressure of the system, the tank material can choose to use carbon steel or glass fiber reinforced plastic.
Four. technical parameter
1. Treatment effect:
①. Fluorine content: ≤0.05mg/L;
②. Turbidity of effluent: <3FTU;
③. Arsenic removal capacity: 10g/kg filter material.
2. Water inlet requirements:
①. Arsenic content: ≤2.0mg/L;
②. Influent turbidity: <50FTU;
③. Alkalinity: ≤2mg/L;
④. pH value: 6-6.5.
3. Working environment parameters
①. Working temperature: 5-60℃ (special temperature can be customized);
②. Working pressure: ≤0.4MPa.
4. Operating parameters
①. Working method: pressure type;
②. Operation mode: water flow from bottom to top, series (high arsenic content) or parallel;
③. Filter material particle size: 0.5-2.5mm;
④. Filtration speed: 5m/h;
⑤ Operation period: 20 days (depending on the quality of the raw water, the minimum is not less than 8 hours);
⑥. Backwashing method: water washing, or air-water combined backwashing;
⑦. Backwash time: 10-15min;
⑧. Water consumption for backwashing: 1-3%;
⑨. Backwash intensity: 18-25l/s·m2;
⑩. Regeneration solution: 2.5-4% sodium hydroxide solution;
⑾. Regeneration time: 10h;
⑿. Regeneration intensity: 8-10L/m2·s;
⒀. Washing time: 8-10min.
five. working principle
1. Process flow
Redox → adsorption and ion exchange → repeated regeneration (backwashing, drug absorption, replacement, forward washing)
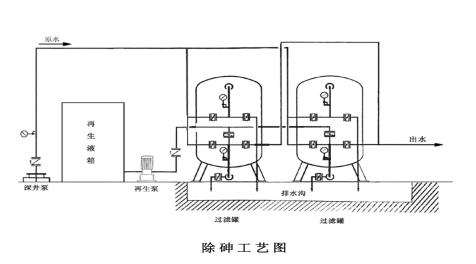
2. working process
①. Redox
Studies have shown that iron salt has better arsenic removal effect than aluminum salt, and the removal effect of As(Ⅴ) is significantly better than As(Ⅲ). Therefore, in the process of arsenic removal, the treated water is often pre-oxidized to reduce trivalent As (Ⅲ) Oxidation to pentavalent As(Ⅴ).
②. Adsorption and ion exchange
Generally, adsorbents for removing arsenic include activated molecular sieves, activated alumina, and bone charcoal. Under the same conditions:
a. Active molecular sieve: the removal rate of trivalent arsenic, 80%; the removal rate of pentavalent arsenic, 95%;
b. Activated alumina: trivalent arsenic removal rate, 70%; pentavalent arsenic removal rate, 80%;
c. Bone charcoal: the removal rate of trivalent arsenic, 25%; the removal rate of pentavalent arsenic, 50%, expensive, easy to cause excessive ammonia nitrogen.
In summary, the results show that active molecular sieve is the most ideal and reliable material for arsenic removal.
③. Repeated regeneration
When the effluent reaches a certain amount, the active molecular sieve will saturate and lose its exchange capacity, and must exit operation for regeneration. At this time, the effluent is provided by other tanks to ensure continuous effluent.
During regeneration, the molecular sieve is required to be backwashed to remove impurities such as suspended solids that may be intercepted, and at the same time to loosen the molecular sieve. Then the liquid medicine is fed from the upper part of the tank, and the regeneration waste liquid is discharged through the drain valve. After the drug washing is finished, the positive washing process is finally carried out to completely remove the residual drug liquid in the molecular sieve layer.
The system can adopt manual and automatic control methods. The working status of each tank is in sequence: running → regeneration (backwashing, inhalation, replacement, forward washing) → running; when the equipment fails, it will automatically exit operation, start the regeneration program, and automatically put it into operation after regeneration. In order to ensure the need for production water, the control system prohibits simultaneous regeneration of the two equipment.
six. Specifications and dimensions
1. Dimensions
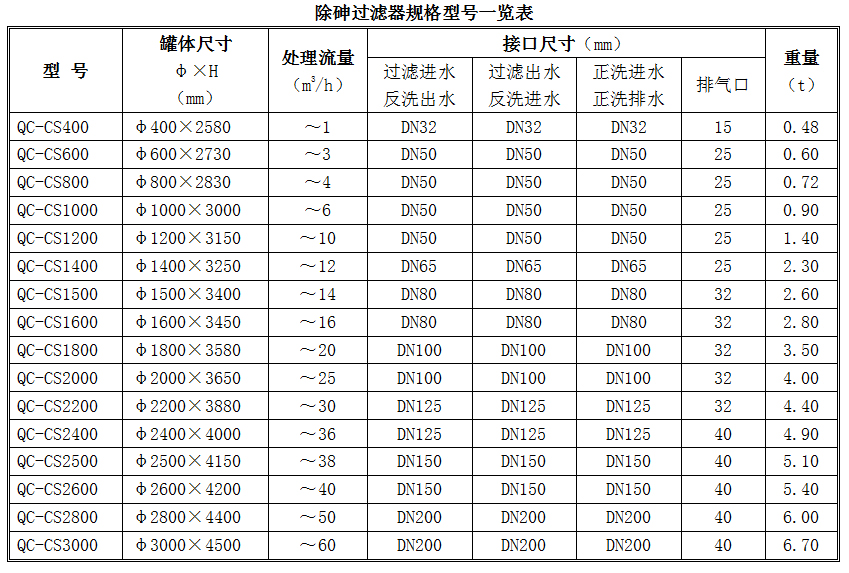
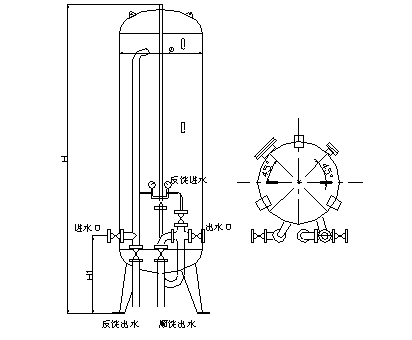 2. List of specifications and models
2. List of specifications and models

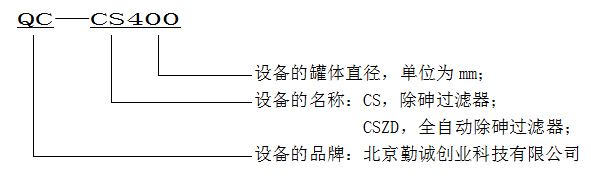
 3. Model Description
3. Model Description

seven. Selection instructions
1. Equipment selection
①. The buyer must provide detailed water quality test reports, water quality usage, automation requirements, machine room size and other basic parameters, so that the supplier can provide detailed equipment selection and filter materials.
②. The primary or secondary treatment system can be selected according to the water quality, and the single or multiple parallel systems can be selected according to the water volume.
③. The process flow of fluorine removal should be determined according to the following conditions:
a. When the raw water contains arsenic ≤ 2mg/L, a single-stage treatment system is adopted;
b. When the arsenic content is greater than 2mg/L, use a secondary treatment system or a treatment system that uses reverse osmosis as the main means to remove arsenic.
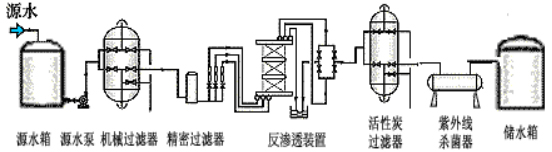
2. device installation
①. The supplier shall provide the relevant operating data of the equipment (such as equipment weight, process flow chart, floor plan, foundation drawing, etc.), and the purchaser shall construct and construct the infrastructure of the equipment by itself based on the relevant operating data provided by the supplier. The concrete floor is poured smoothly, and the error does not exceed 10mm.
②. Calibrate the equipment smoothly, and the error shall not exceed 10mm, so that the equipment can run uniformly and stably.
③. Fill the filter material evenly, and install the filter material according to the design index and filter material specifications.
④. Install the supporting facilities of the equipment body such as pipelines and valves according to the design procedures, and check whether there is any leakage. If yes, perform emergency maintenance; if not, perform debugging.
⑤. Clean the filter element and filter material, open the filtered water and drain valve in turn, clean before operation, and wait until the cleaning water of the filter layer becomes clear. Check whether the equipment is running well.
⑥. Open the water inlet pipe and control the water inlet water volume so that the water inlet water volume meets the design flow rate. Take a clean water sample and open the clean water valve when the fluorine content is ≤ 1.0mg/L.
⑦. Debug the backflush pump, close the filter inlet and outlet pipe valves, open the backwash water inlet pipe and backwash outlet pipe valves. After the water discharged from the outlet pipe becomes clear, the backflush ends. Restart and operate normally.
- Previous Article: Fluoride filter
- Next Article: Ammonia nitrogen filter